"Molecular Structure of Nucleic Acids A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid" was the first article published to describe the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA, using Xray diffraction and the mathematics of a helix transform It was published by Francis Crick and James D Watson in the scientific journal Nature on pages 737–738 of its 171st volume (dated 25 April 1953)The Structure of DNA Nucleic acids are made up of chains of many repeating units called nucleotides (see bottom left of Figure 1 below) The DNA molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix (spiral) Nucleic acid molecules are incredibly complex, containing the code that guarantees the accurate ordering of theThe structures in the diagram labeled W are ?
Primer Molecular Biology Wikipedia
Double stranded dna molecule diagram labeled
Double stranded dna molecule diagram labeled- · Photo 51 The xray diffraction image that led to the discovery of the doublehelical structure of DNA Photograph King's College LondonA Identify the building blocks of DNA and label the parts in the diagram building block nucleotide B Identify the number of DNA strands found in a DNA molecule and Explain the orientation of the DNA strands 2 DNA strands hydrogen bonded together the 2 strands are antiparallel C Identify and label the following parts in a DNA molecule



Pin On Health And Medicine Illustrated
Structure of DNA Thymine the nucleotide that hydrogen bonds with the nucleotide adenine in DNA DNA Structure and Replication34 Label The Dna Molecule The dna molecule actually consists of two such chains that spiral around an imaginary axis to form a double helix spiral nucleic acid molecules are incredibly complex containing the code that guarantees the accurate ordering of the amino acids in all proteins made by living cellsMolecules containing the psoralen functional group can be used to label doublestranded DNA or RNA The psoralen ring structure effectively intercalates into the doublestranded portions, and exposure to UV light causes a cycloaddition product to be formed with the 5,6double bond in thymine residues
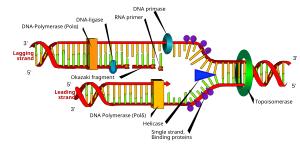
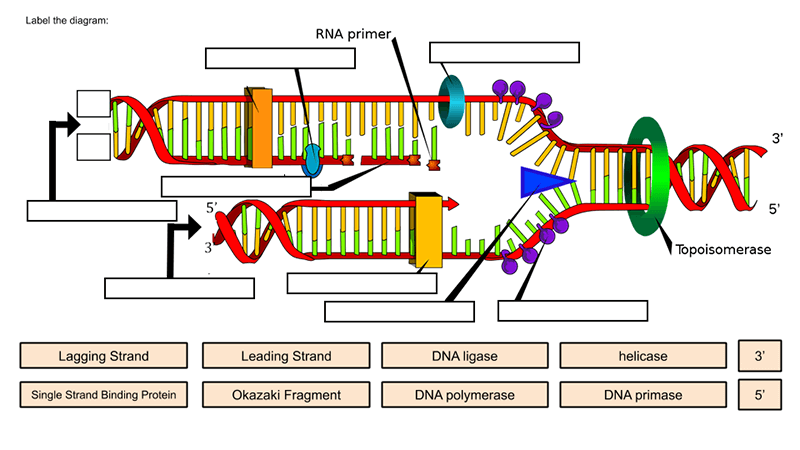
· The 3 end of a dna strand has an exposed oh group and the 5 end has a phosphate group The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental dna Nucleic Acids Helicase is the enzyme which cause the dna molecule to unzip The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental dna In the labels the original parental dna is · In our singlemolecule experiment, we used a DNA concentration of 100 pM to make sure that at most only one molecule was present in the focal volume within the detection time window of 600 μsWe used a buffer that contains 50 mM pH 8 Tris, 1 mM MEA, and 5 vol% glycerolThe salt concentration was varied from 10 mM to 2 M 22Subscribe Nowhttp//wwwyoutubecom/subscription_center?add_user=ehoweducationWatch Morehttp//wwwyoutubecom/ehoweducationDNA is two different strands of
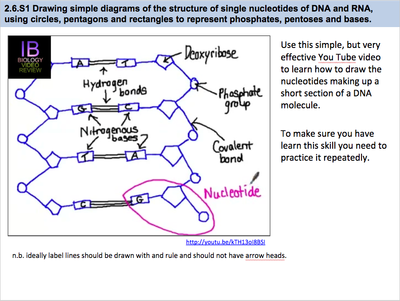
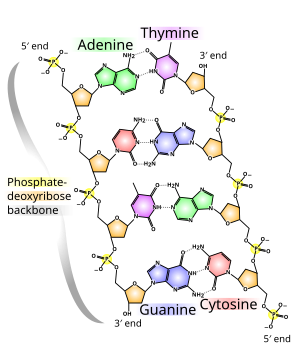
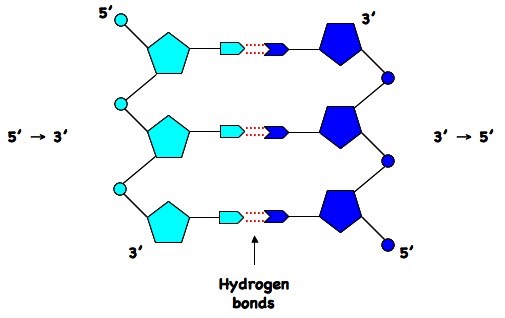
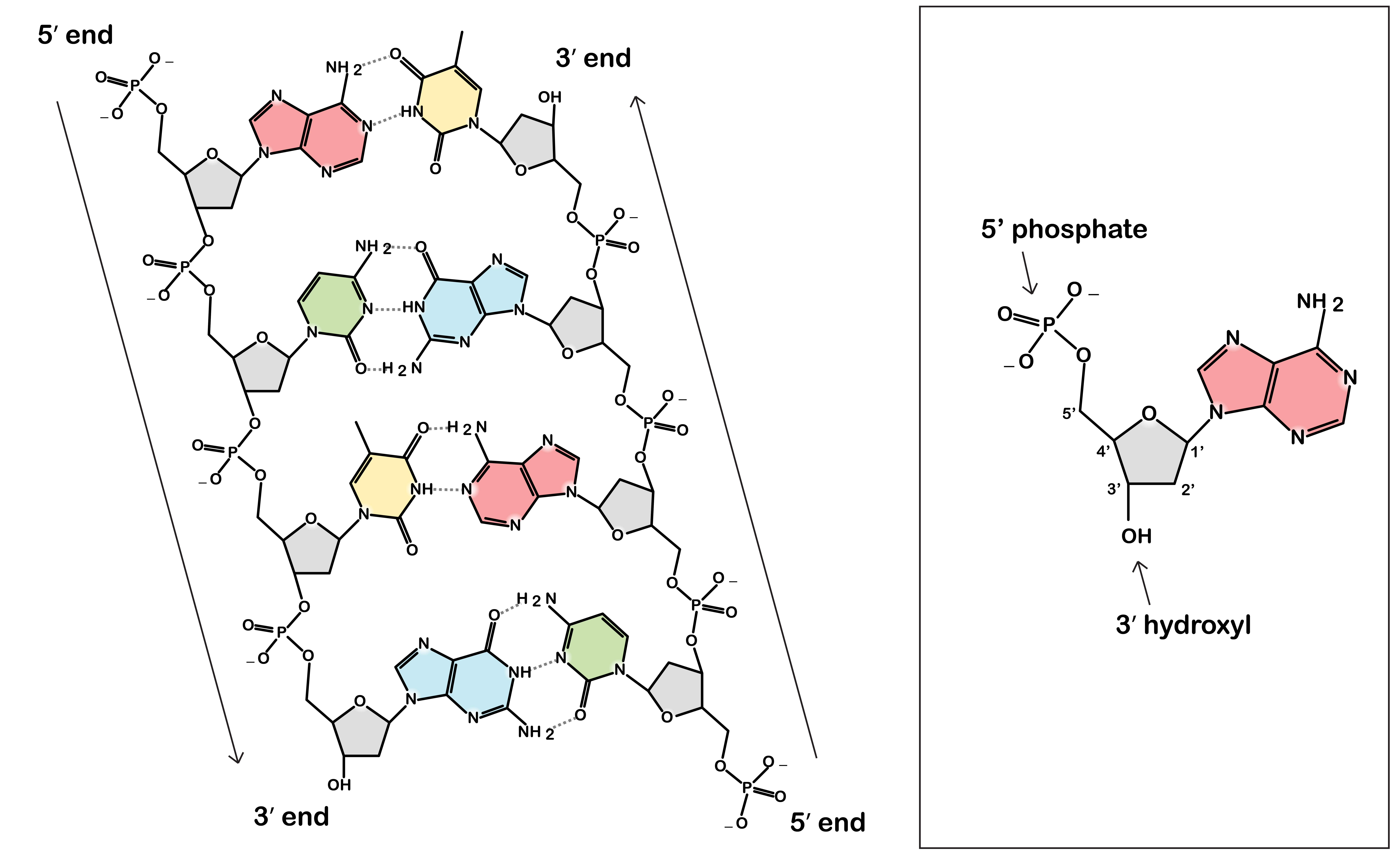
Diagram showing how the two strands of double stranded DNA runs antiparallel to each other One strand runs in a 3' to 5' direction while the other runs in a 5' to 3' direction The nucleotides forming each DNA strand are connected by noncovalent bonds, called hydrogen bondsNucleic acids may be labeled at their 5´ end, their 3´ end, or throughout the molecule depending on the application For hybridization reactions (Southern or northern blotting) it is usually advantageous to generate high specific activity probes with label distributed throughout the nucleic acid, through techniques such as nick translation, random priming, by PCR or in vitroTranscribed image text A) The diagram below represents an untwisted, doublestranded DNA molecule 5 pts Label each sugar group on the diagram with a letter S 2 Label each phosphate group with a letter P 3A, T, C and G have already been labeled Match and label the rest of the nitrogenous bases 4 Circle one nucleotide What three things go together to make a nucleotide?



Storing Genetic Information Biology For Non Majors I



With The Help Of A Neat And Labeled Diagram Describe Waston And Crick S Model Of Dna
The structures in the diagram labeled X are ? · This stress is removed and strands are separated by the action of DNA topoisomerase Topoisomerase I introduces cut or nick in one DNA strand Topoisonmerase II remove supercoils by causing double stranded breaks Some parts of DNA molecule have circle linked as a chain This structure is called catenane · The parental dna is shown in dark blue the newly synthesized dna is light blue and the rna primers associated with each strand are red The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental dna Part a the mechanism of dna replication the diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental dna I am new with this


2 6 Dna Rna Structure



2 6 And 2 7 Paper 2 Questions Flashcards Quizlet
The structures in the diagram labeled W are ? · Thus the labeled fragment described here may be displaced by DNA and RNA polymerases and proteins that translocate along double‐stranded DNA Therefore, the labeled fragment could be an interesting tool for the study of protein movement and may be used as a probe for observing their one‐dimensional motion In conclusion, the labeling strategy described in this paper represents an original approach for the visualization of short sequences of double‐stranded DNAA quick look at the whole structure of DNA These days, most people know about DNA as a complex molecule which carries the genetic code Most will also have heard of the famous double helix I'm going to start with a diagram of the whole structure, and then take it



Sketch And Label Only A Double Helical Dna Molecule Brainly In


Dna Drag And Drop
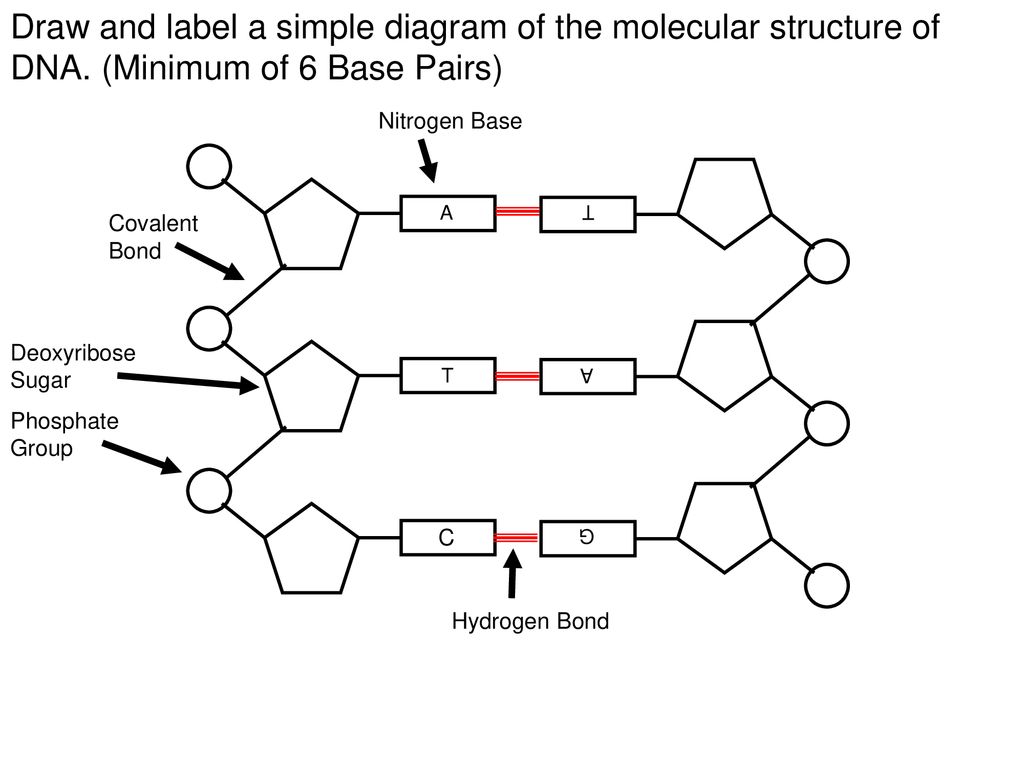
· 12 Flexibility of DNA Molecule as a Polymer The DNA molecule is a longchain polymer that consists of two antiparallel polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix 8,9NonBDNA structures, such as Aform or Zform, are induced by a high salt or high ethanol concentration 10,11,12, whereas the double helix of DNA in an aqueous solution ofDoublestranded DNA template comprising T7 RNA polymerase promoter (sequence of template strand is 5′TTCTTATCTT CCAAGCTGTT CGAGCTTGCT GGATTTAGCA CCTTGGTCAT GGCTGATCGC CATTACACCG GTTGCTGAAG CTTCGTCGGG CCAGTCCCTC TATAGTGAGT CGTATTACAG3′, T7 RNA polymerase promoter in italics), Buffers and reagents (1 M Tris–HCl,Draw a labelled diagram to show how four nucleotides are joined together to form a doublestranded DNA molecule with two base pairs 3 b State two differences between RNA linkages correctly shown;



Schematic Of The Fret Standard Molecules Double Stranded Dna Was Download Scientific Diagram


Dna Wikipedia
DNA fragments were synthesized consisting of 12 nucleotides and containing nonnucleotide inserts of different length in the middle Two nitroxide spin labels 4amino2,2,6,6tetramethylpiperidine1oxyl were attached at the two ends of the molecules Singlestranded DNAs and doublestranded DNAs (DNA duplexes) in frozen at 77 K glassy water / glycerol · ZDNA is a radically different duplex structure, with the two strands coiling in lefthanded helices and a pronounced zigzag (hence the name) pattern in the phosphodiester backbone As previously mentioned, ZDNA can form when the DNA is in an alternating purinepyrimidine sequence such as GCGCGC, and indeed the G and C nucleotides are in differentDouble helix is the description of the structure of a DNA molecule A DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder Each strand has a backbone made of alternating groups of sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate groups Attached to each sugar is one of four bases adenine (A), cytosine , guanine (G), or thymine (T)


Open Genetics Cubocube



Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology
Details Transcribed image text A) The diagram below represents an untwisted, doublestranded DNA molecule 5 pts Label each sugar group on the diagram with a letter S 2 Label each phosphate group with a letter P 3A, T, C and G have already been labeled · In a double stranded DNA molecule, the two strands run antiparallel to one another so that one strand runs 5′ to 3′ and the other 3′ to 5′ The phosphate backbone is located on the outside, and the bases are in the middle Adenine forms hydrogen bonds (or base pairs) with thymine, and guanine base pairs with cytosine · RNA, like DNA, can form double helices held together by the pairing of complementary bases, and such helices are ubiquitous in functional RNAs Here we apply external forces and torques to individual doublestranded RNA molecules to determine the mechanical properties and conformational transitions of these fundamental biological building blocks For



Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable
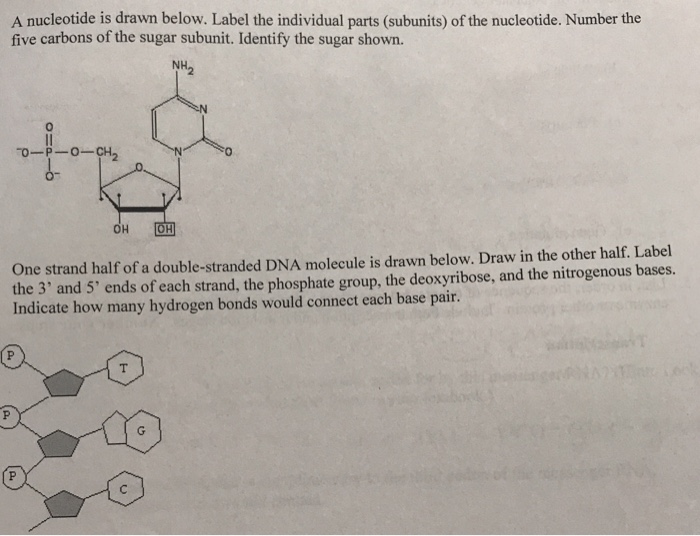


Solved A Nucleotide Is Drawn Below Label The Individual Chegg Com
DNA Molecule Label STUDY Learn Flashcards Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Molecule found on the side of a DNA molecule Double Helix two strands of nucleotides wound about each other; · The Diagram Below Represents A Portion Of Double Stranded Dna Molecule Posted on March 28, 19 by admin The diagram below represents a simple model of gene promoter and terminator are labeled for you use this to answer following questions download figure dna diagram of dna replication a circle double stranded has region labeled ssoThe doublestranded structure of DNA provides a simple mechanism for DNA replication Here, the two strands are separated and then each strand's complementary DNA sequence is recreated by an enzyme called DNA polymerase This enzyme makes the complementary strand by finding the correct base through complementary base pairing and bonding it onto
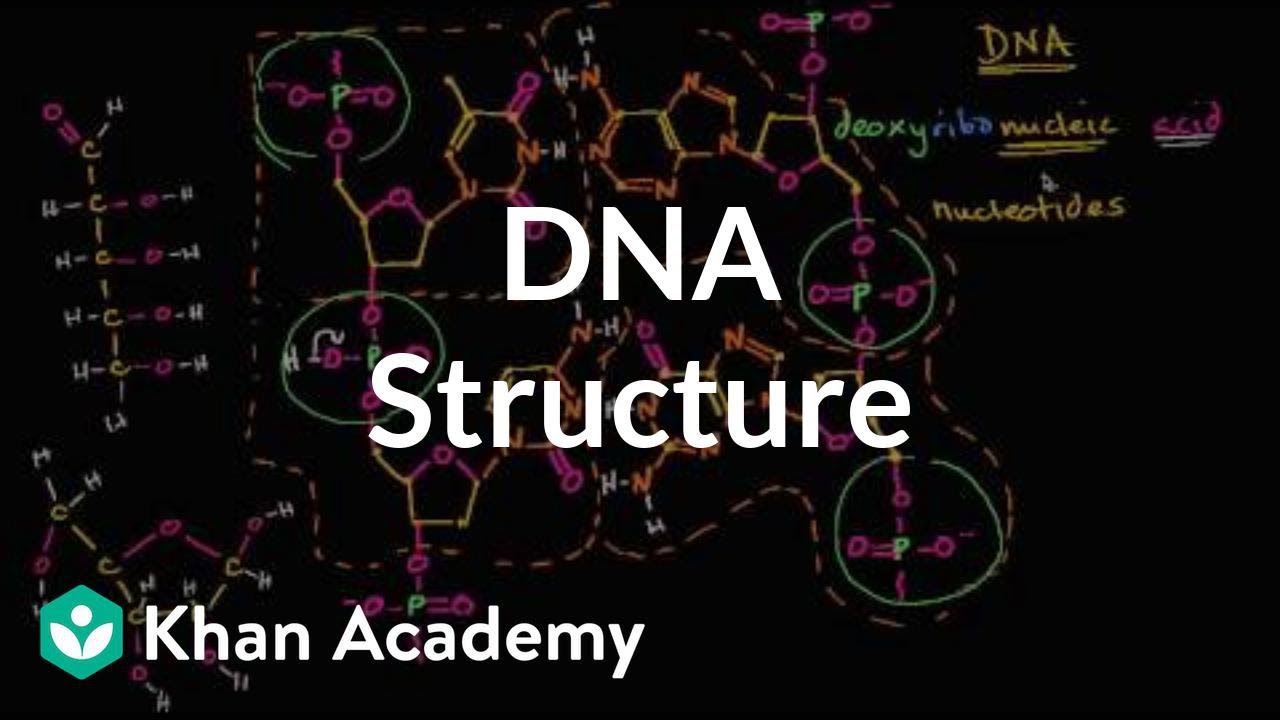


Molecular Structure Of Dna Video Khan Academy


Life Sciences Cyberbridge
Rolling circle replication begins with the enzymatic nicking of one strand of the doublestranded circular molecule at the doublestranded origin (dso) site In bacteria, DNA polymerase III binds to the 3′OH group of the nicked strand and begins to unidirectionally replicate the DNA using the unnicked strand as a template, displacing the nicked strand as it does soThe structures in the diagram labeled X are ? · Glossary deoxyribose a fivecarbon sugar molecule with a hydrogen atom rather than a hydroxyl group in the 2′ position;



Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable


Dna Molecule Two Views
The doublestranded DNA molecule has a three dimensional structure known as a ? · Filling duplexes I and III with BrdUTP (resulting in IBr and IIIBr, Figure Figure1C)1C) yields an internally double labeled DNA molecule containing two BrdU residues separated by 3 bp In principle, the same or different classIIS REases, producing 5' protruding 4nt cohesive ends, could be used for the cleavage of PCR1 and PCR2(no label required) b RNA nucleotides contain ribose and DNA The diagram shows part of a DNA molecule What type of bond does X represent
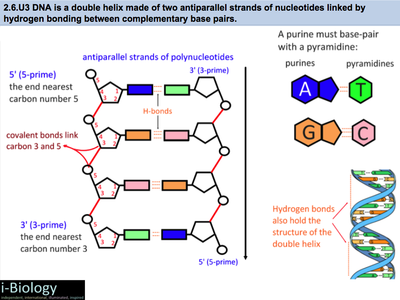


2 6 Dna Rna Structure



Dna Structure And Sequencing Cell Biology Openstax Cnx
Cially designed to prepare long DNA duplexes labeled with HalNBs Results and discussion General idea The incorporation of one or two molecules of 5BrdU per molecule of synthetic duplex taking place in the abovementioned process is illustrated schematically in Figure 1 Let us assume that two doublestranded DNA/10/16 · The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental duplex The parental dna is shown in dark blue the newly synthesized dna is light blue and the rna primers associated with each strand · Thus the labeled fragment described here may be displaced by DNA and RNA polymerases and proteins that translocate along doublestranded DNA Therefore, the labeled fragment could be an interesting tool for the study of protein movement and may be used as a probe for observing their onedimensional motion In conclusion, the labeling strategy
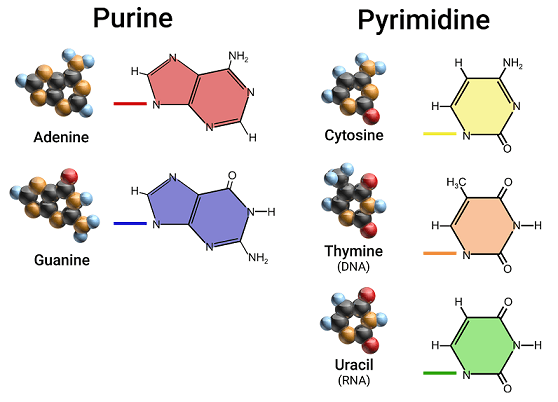


Dna Structure Overview Diagrams Expii
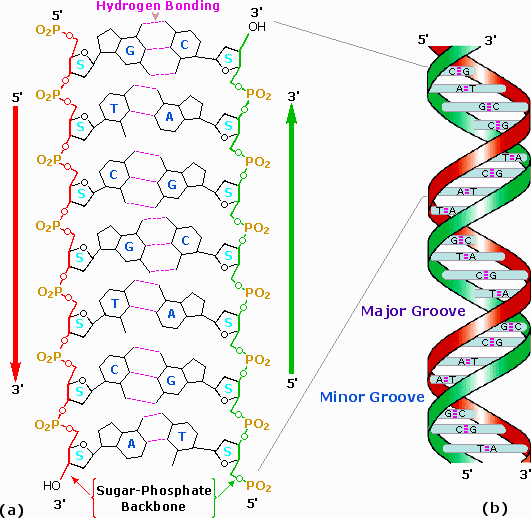


Nucleic Acids
The doublestranded DNA molecule has a three dimensional structure known as a ?The DNA of E coli appears to consist of a single, enormous doublestranded DNA molecule with a molecular weight of about 28 x 10 9, a thickness of about nm and a contour length of about 1,360µm E coli DNA contains 4 million deoxyribonucleotide pairsDoublestranded DNA, we hold and extend the molecule In our initial set of experiments, focusing on the overstretching transition occuring at 65 pN, we use lambda DNA that is linked to the microspheres with one of the strands on either side of the DNA (designated 3 3 attached DNA) (see Fig 1A) We set out to
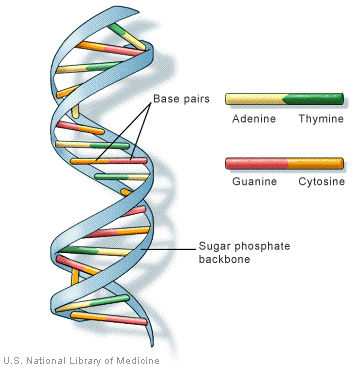


Dna Structure
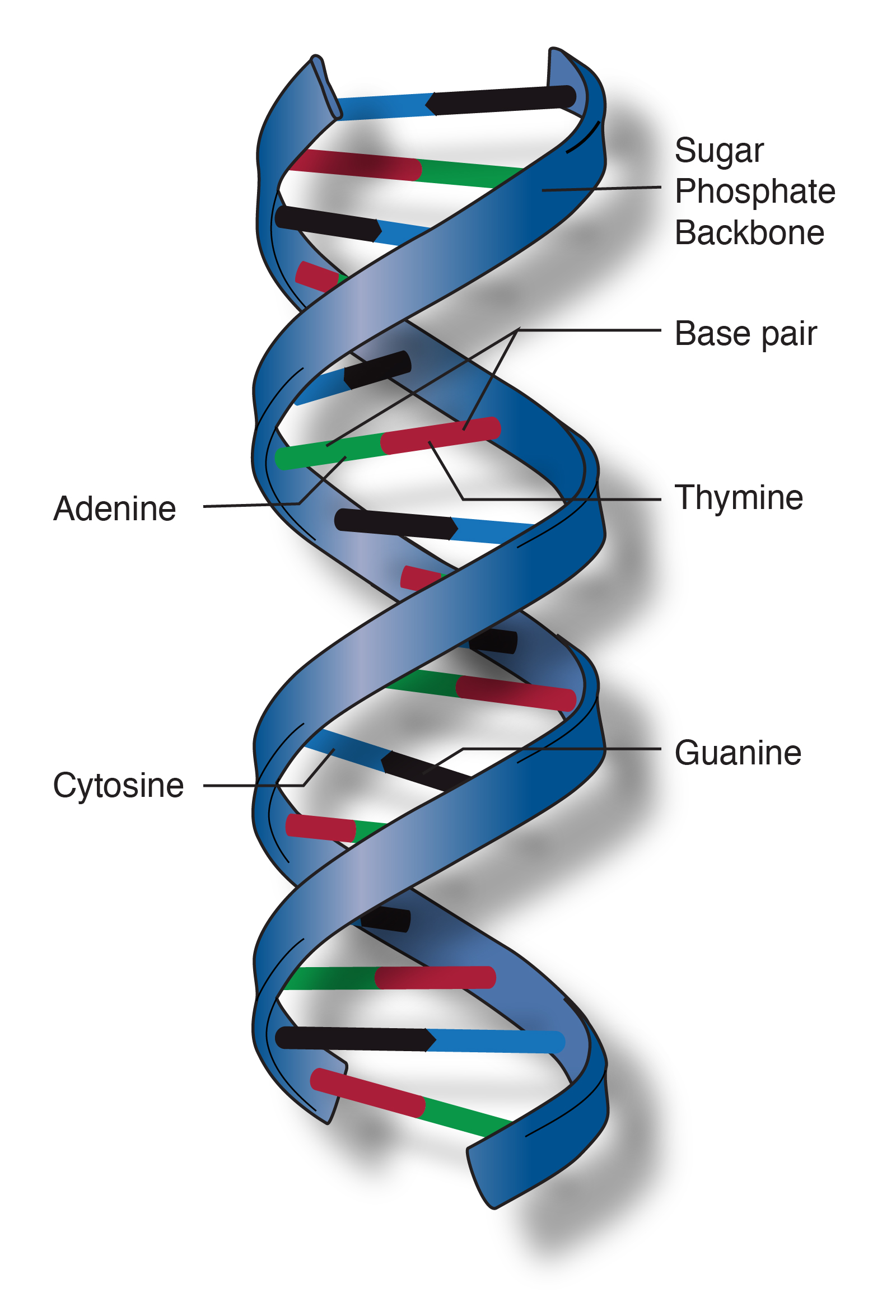


Dna Double Helix
The sugar component of DNA nucleotides double helix the molecular shape of DNA in which two strands of nucleotides wind around each other in a spiral shape nitrogenous base a nitrogencontaining molecule that acts as a base;Which part of the DNA molecule contributes to the property? · DNA Structure DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid is a type of molecule known as a nucleic acid It consists of a 5carbon deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base Doublestranded DNA consists of two spiral nucleic acid chains that are twisted into a double helix shape This twisting allows DNA to be more compact



Dna Structure Dna Replication Biology Online Tutorial


The Structure Of Dna
Figure 2 (a) DNA is typically double stranded, whereas RNA is typically single stranded (b) Although it is single stranded, RNA can fold upon itself, with the folds stabilized by short areas of complementary base pairing within the molecule, forming a threedimensional structureThe basic unit of DNA, the nucleotide, is made up of one of each A molecule of DNA may contain as many as 0,000 nucleotides The nucleotides make up two chains that are linked and twisted around one another in the form of a double helix OBJECTIVES In this activity you will Learn the basic units and structure of DNA · The diameter of the DNA double helix is uniform throughout because a purine (two rings) always pairs with a pyrimidine (one ring) and their combined lengths are always equal (Figure 913) Figure 913 DNA (a) forms a double stranded helix, and (b) adenine pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine


The Structure Of Dna
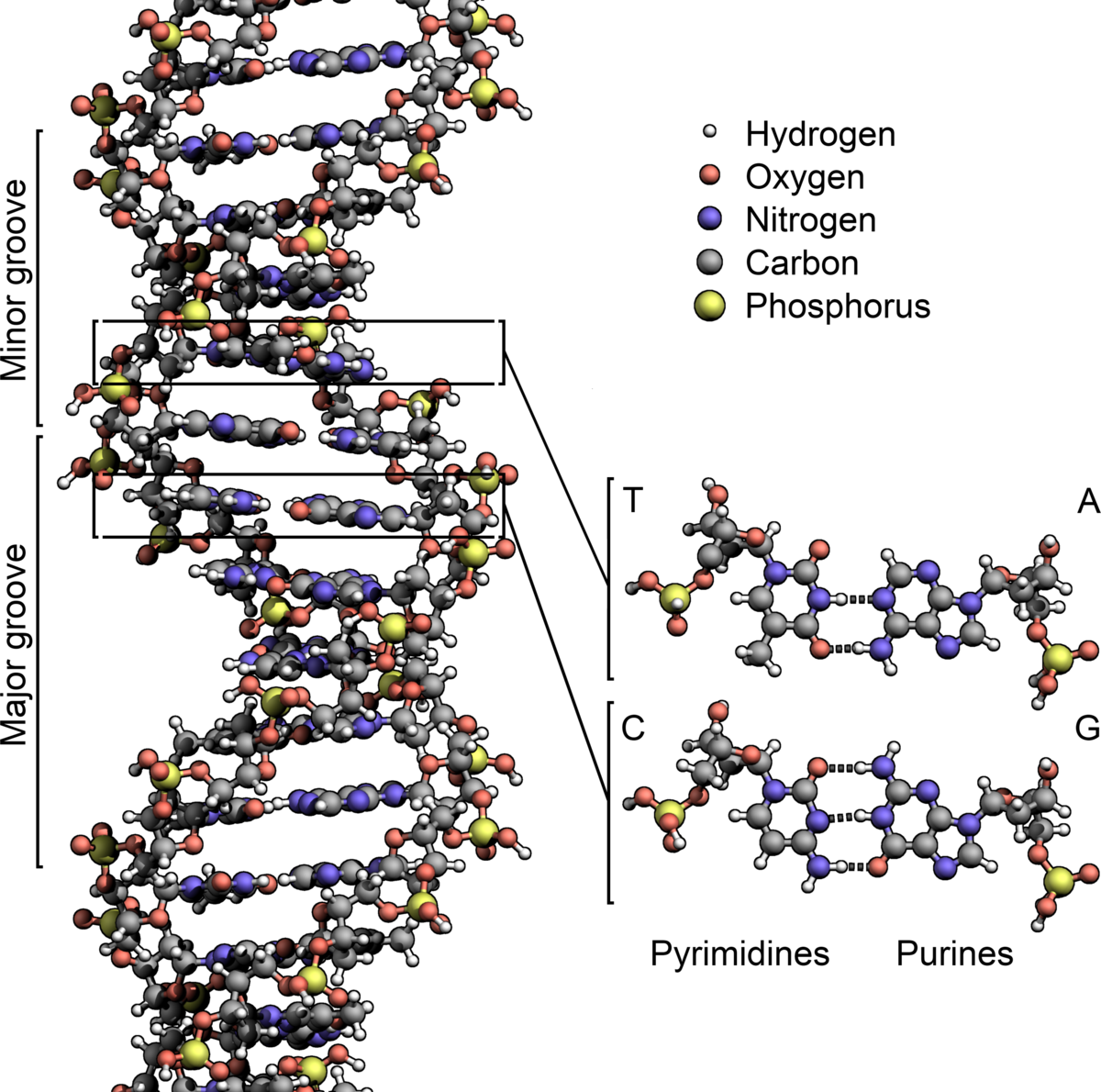


Dna Wikipedia
· The diagram below shows a double stranded dna molecule parental dna As we know cell division is essential for an organism to grow but when a cell divides it must replicate the dna dna replication take place during s phase in its genome so that the two daughter cells have the same genetic information as their parentThis enzyme introduces a singlestrand nick in the DNA, enabling it to swivel and thereby relieve the accumulated winding strain generated during unwinding of the double helixSingle Strand Binding Proteins Responsible for holding the replication fork of DNA open while polymerases read the templates and prepare for synthesis · In DNA replication, the double helix unwinds and each separated strand is used to synthesize a new strand As the new strands form, bases are paired together until two doublehelix DNA molecules are formed from a single doublehelix DNA molecule DNA replication is required for the processes of mitosis and meiosis to occur


Ch02 Nucleic Acids And Atp



Sohn Unit 4 Dna Flashcards Quizlet
Draw the chemical structure of the following doublestranded DNA molecule Then, identify and label the bonds that exist in the DNA molecule you have drawn 5' ATTG IIII TAAC 5 ii What is the net charge of the DNA molecule? · To prepare this biotinlabeled segment (∼559 bp), doublestranded DNA fragments (600 bp) were first obtained using PCR amplification with pUC18 plasmid as a template We designed the primers such that the PCR products contained the restriction sites near the end of the strands, allowing us to remove the digested useless short DNA fragments via the PCR



Pin On Health And Medicine Illustrated



Diagram Of A Dna Structure Labelled Diagram Of Dna Structure Class 12 Biology Youtube In 21 Biology Diagram Dna
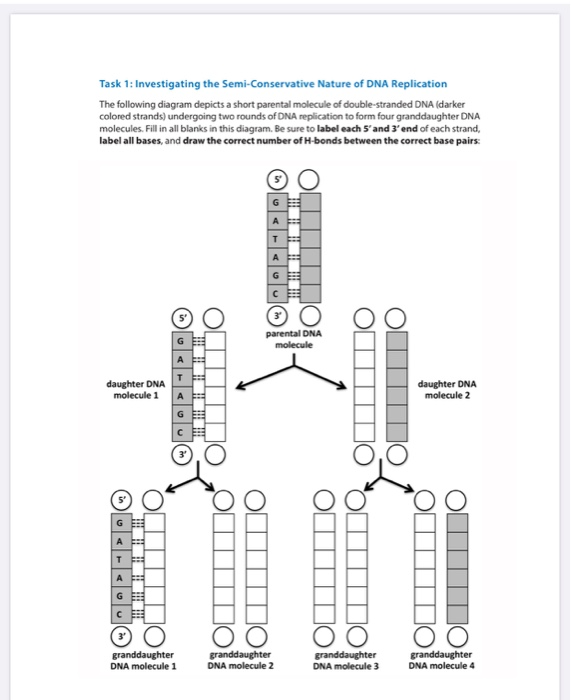


Solved Task 1 Investigating The Semi Conservative Nature Chegg Com


Life Sciences Cyberbridge



With The Help Of A Neat And Labelled Diagram Describe Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna Biology Shaalaa Com



Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks



Primer Molecular Biology Wikipedia



Dna Structure Interactive Tutorial Sciencemusicvideos



Dna Structure And Function Dna Structure And Function
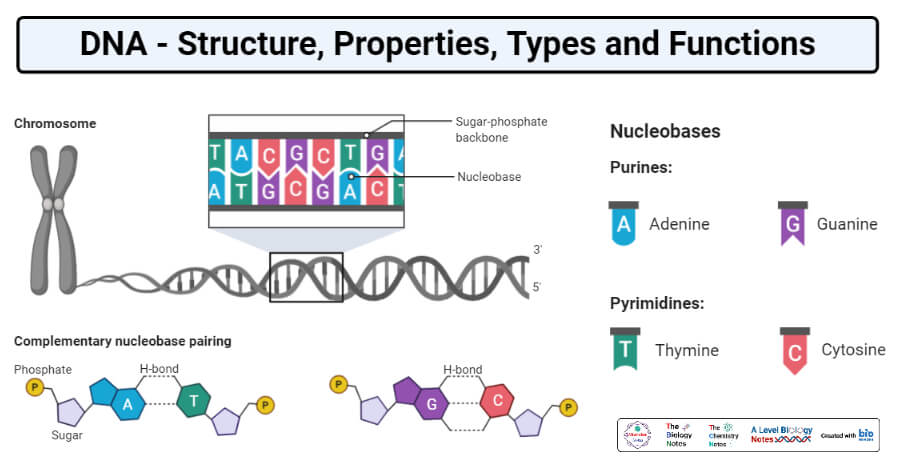


Dna Structure Properties Types Forms Functions



3 3 5 Draw A Simple Diagram Of Dna Structure Youtube
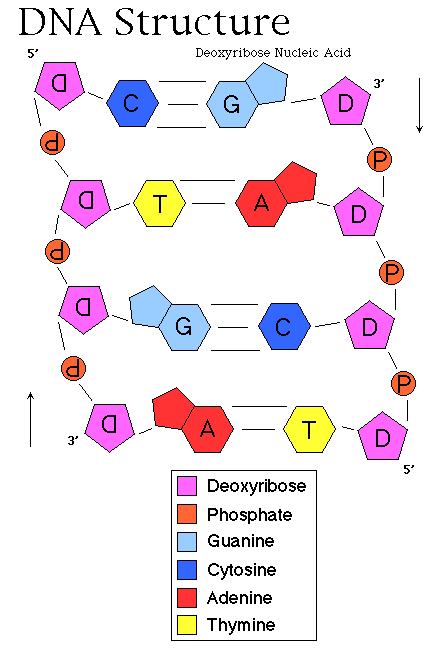


Dna Structure
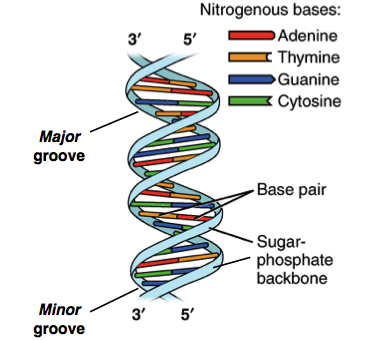


Dna Structure And Replication Review Article Khan Academy


The Structure Of Dna



Structure Of Ll37 Double Stranded Dna Dsdna Complexes From Download Scientific Diagram


Dna Structure Bioninja



Draw It Neat How To Draw Dna



Can Someone Please Draw Me A Dna Model Then Label Each Material And The Part Of The Dna Molecule It Brainly Com



A The Diagram Below Represents An Untwisted Chegg Com



2 6 And 2 7 Paper 2 Questions Flashcards Quizlet



Upper Schematic Representation Of The Experiment A Digbiotine Download Scientific Diagram



Molecular Structure Of Nucleic Acids A Structure For Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Wikipedia


Dna And Molecular Genetics



Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy
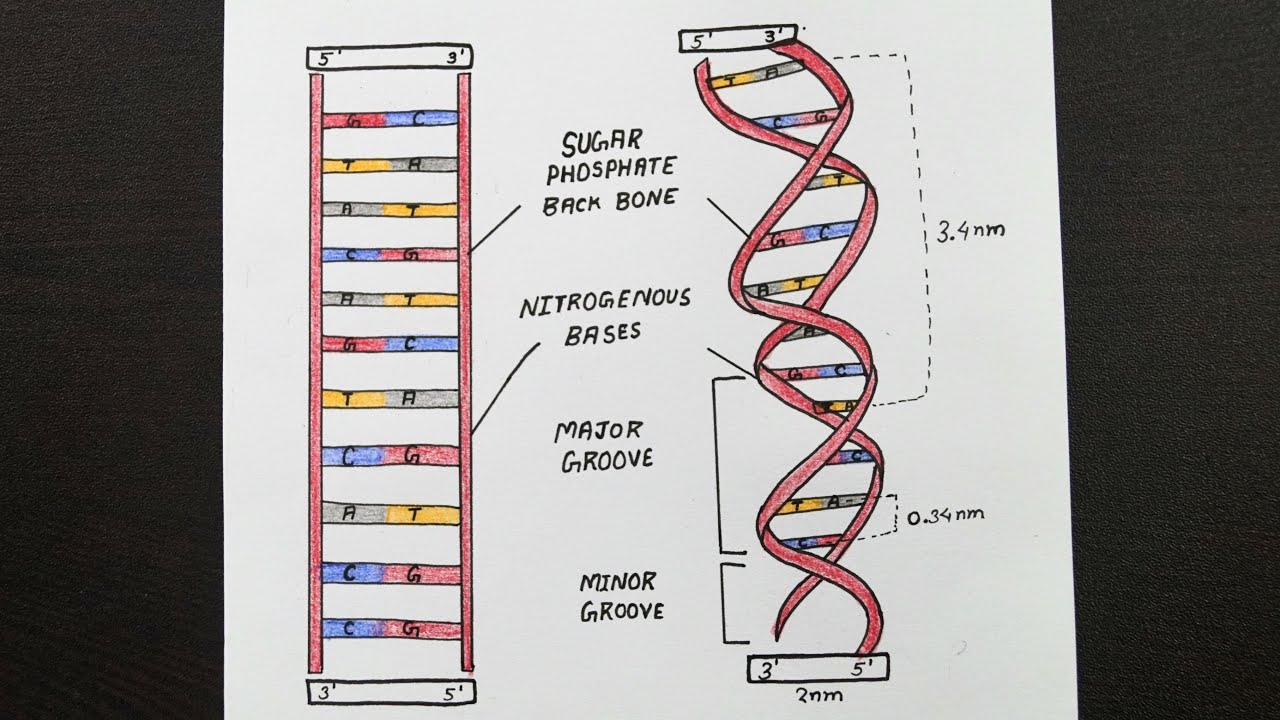


Diagram Of A Dna Structure Labelled Diagram Of Dna Structure Class 12 Biology Youtube


3 3 Dna Structure Bioninja
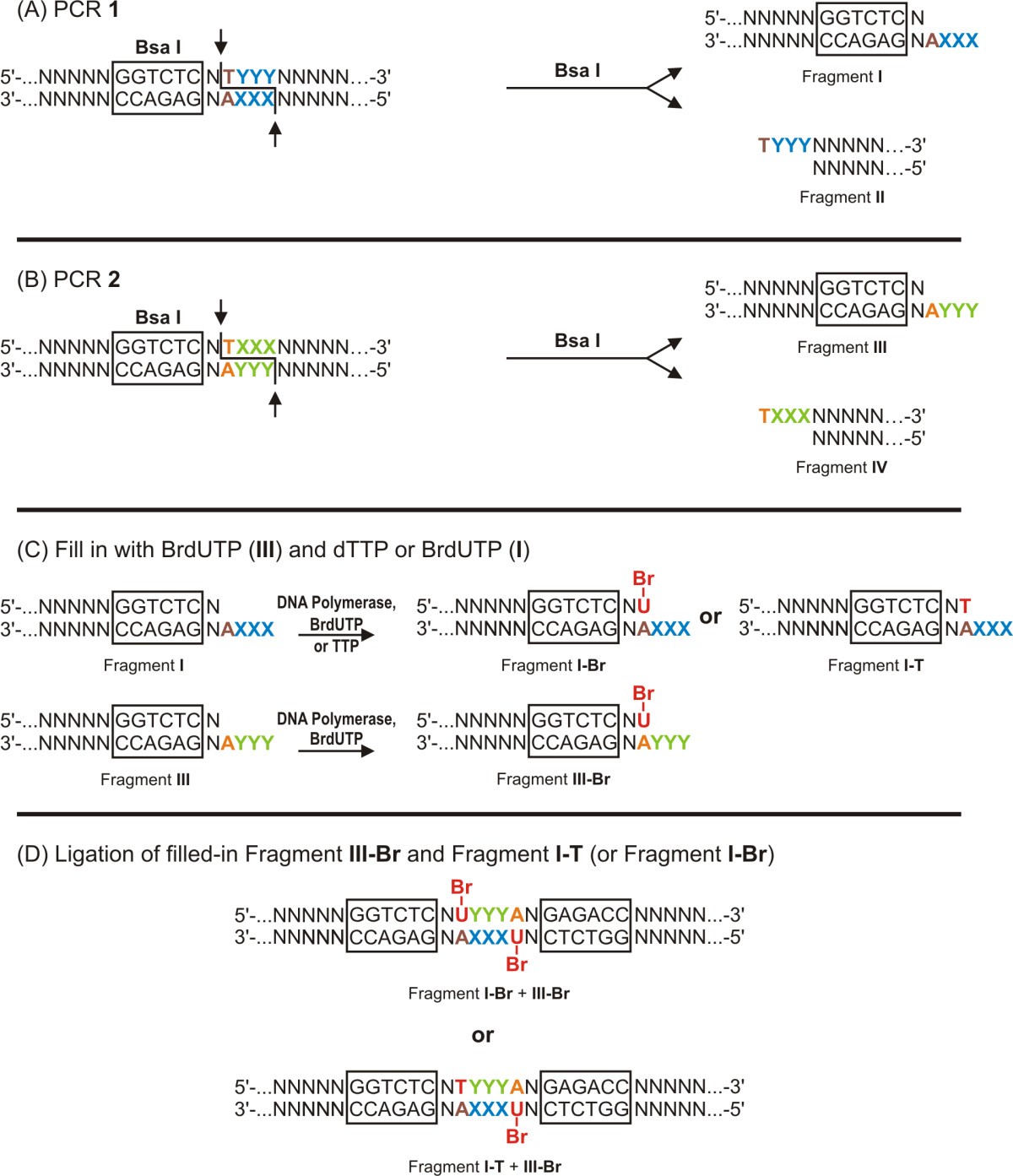


Enzymatic Synthesis Of Long Double Stranded Dna Labeled With Haloderivatives Of Nucleobases In A Precisely Pre Determined Sequence Bmc Biochemistry Full Text
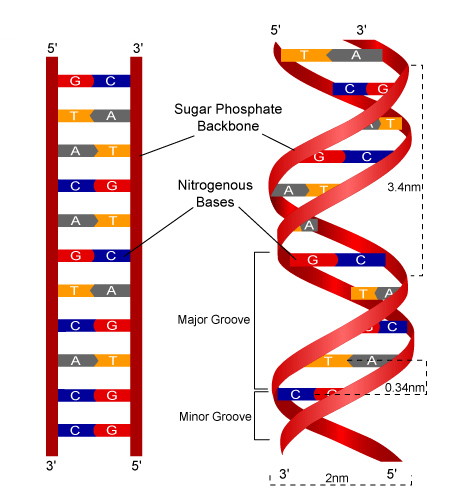


Dna Structure



Make A Candy Dna Model Stem Activity


Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy



Dna Structure And Function Dna Structure And Function



Dna Molecule Label Diagram Quizlet



Dna Sammisbiologyblog


Dna Structure Contexo Info


33 Draw And Label A Dna Molecule Labels Database



Double Stranded Dna Homology Produces A Physical Signature Pnas



7 Repetitive Shuttling Of Rep Helicase On Single Stranded Dna Ssdna Download Scientific Diagram



Dna Replication Microbiology


The Structure Of Dna



A The Left Diagram Shows How An Individual Double Stranded Dna Molecule Download Scientific Diagram



Double Stranded Dna Detailed Structure Download Scientific Diagram



New Dna Rna Tool To Diagnose Treat Diseases Nasa
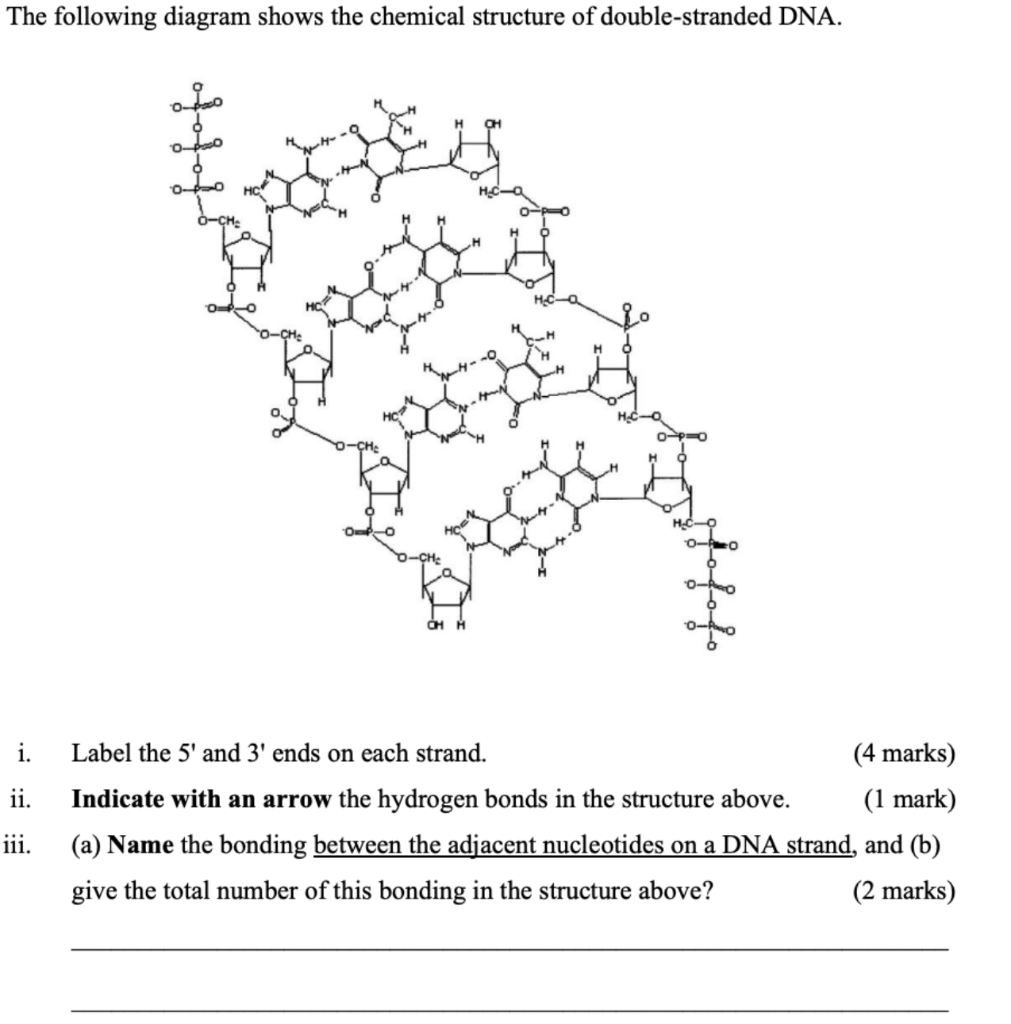


Solved The Following Diagram Shows The Chemical Structure Chegg Com


Notes Dna Structure Topic Ppt Download



Dna Replication Labeled Dna Replication Dna Research Science Biology


Dna Replication With Diagram Molecular Biology
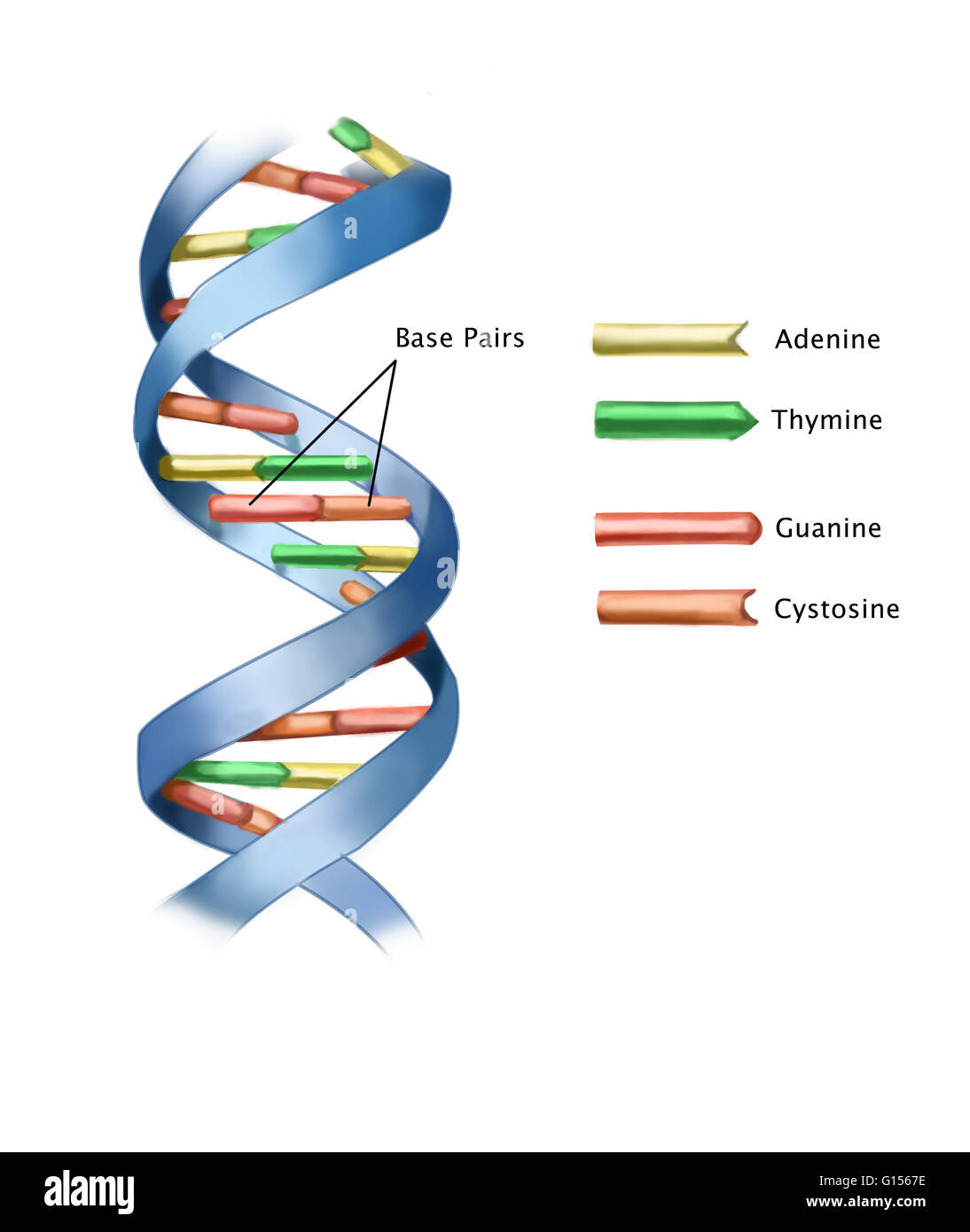


Illustration Of Part Of A Strand Of Dna Deoxyribonucleic Acid Featuring Labeled Base Pairs The Dna Molecule Has A Double Helix Arrangement Being Composed Of Two Right Handed Spiral Strands Of Sugar Phosphates


Dna The Fundamental Molecule To The Organization Of Life Is Deoxyribonucleic Acid Or Dna Dna Is A Complex System Of Chemicals Bonded In Such A Way That They Spell A Code That Defines Who We Are The Entire Human Genome Or Genetic Code Is
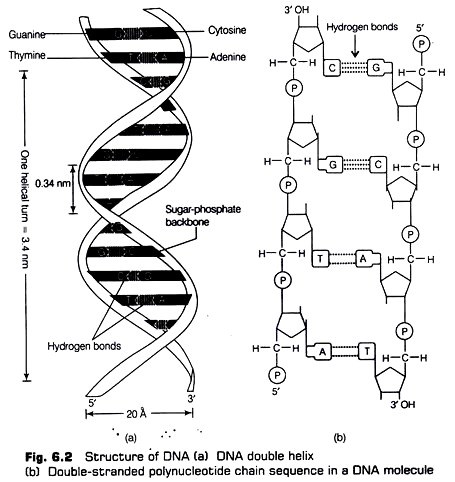


33 Dna Structure Label Labels Design Ideas
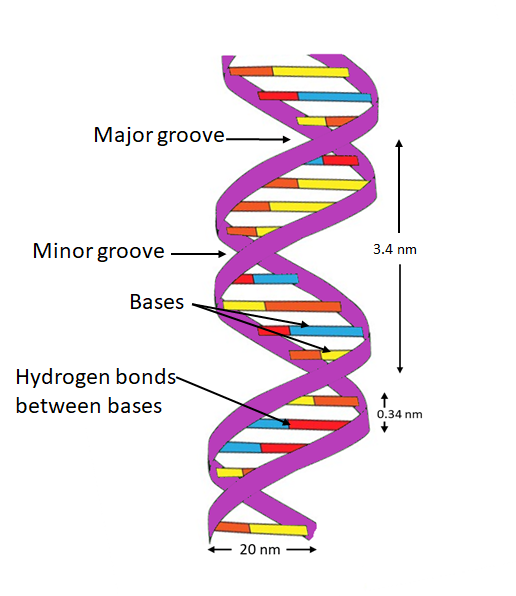


Explain The Double Helix Structure Of Dna With A Labeled Class 10 Biology Cbse



The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna



1 Schematic Representation Of Double Stranded Dna The Double Helix Download Scientific Diagram
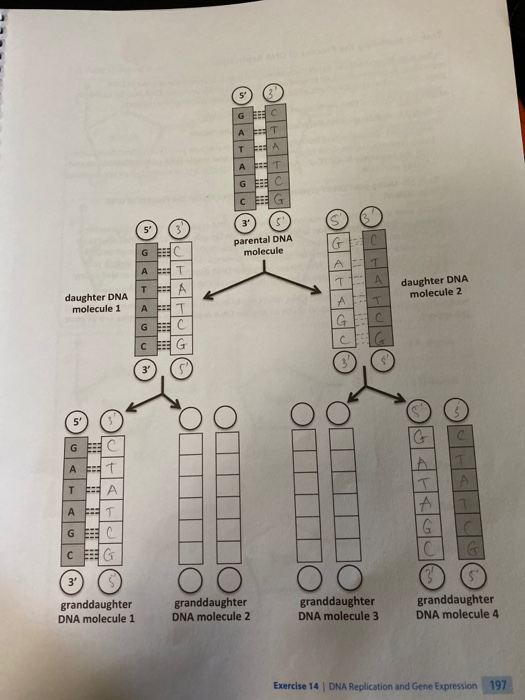


Solved Fill In All Blanks In This Diagram Be Sure To Lab Chegg Com



Dna Replication Microbiology
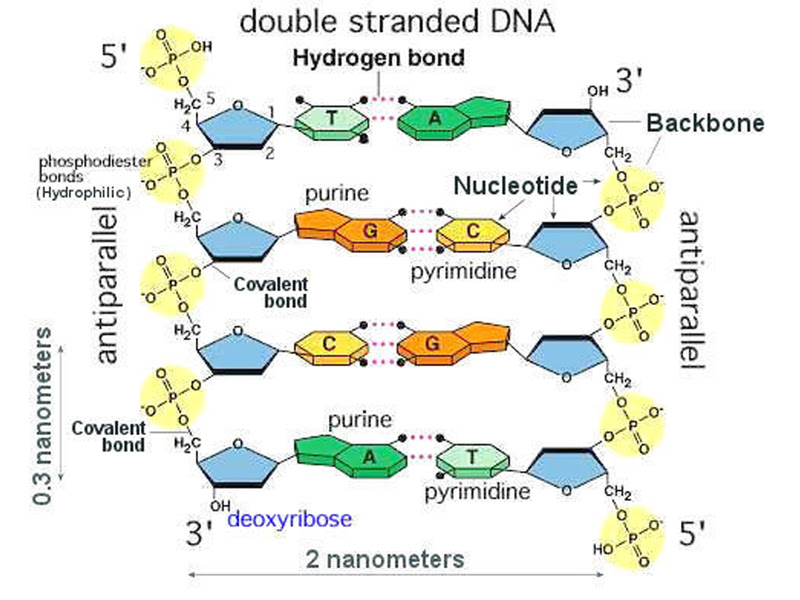


34 Can You Correctly Label Various Parts Of A Dna Molecule Labels For You
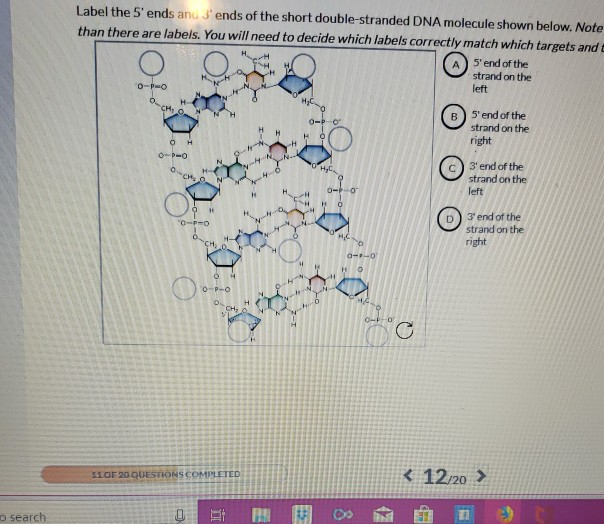


Solved Label The 5 Ends Anu J Ends Of The Short Double Chegg Com
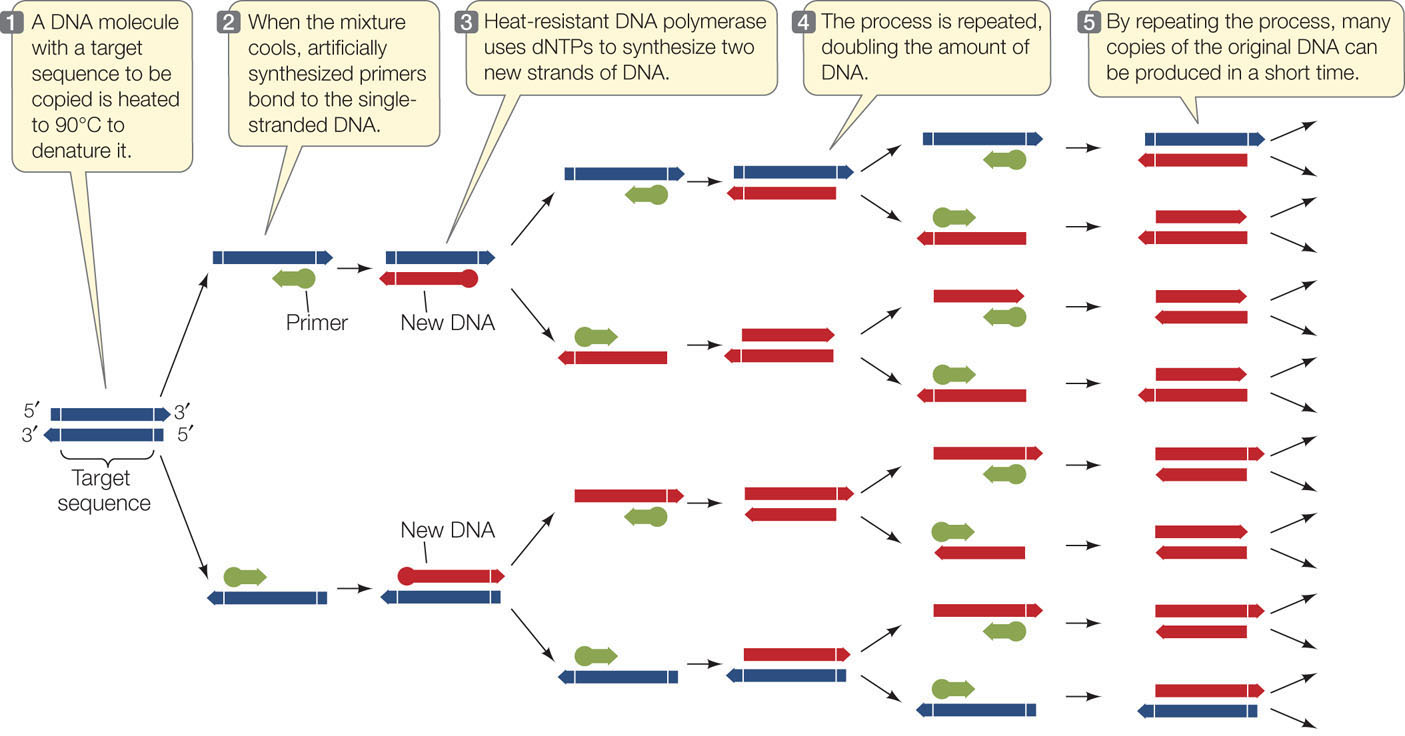


Hillis2e Ch09



Dna Genes And Chromosomes University Of Leicester



Dna Structure Overview Diagrams Expii



Dna Structure Labeling Diagram Quizlet
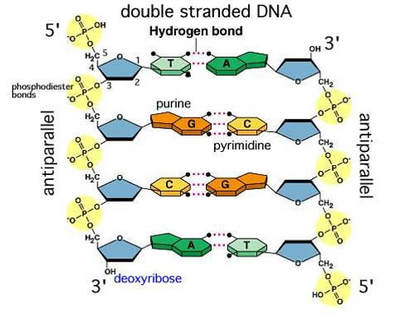


2 6 Dna Rna Structure



Dna Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
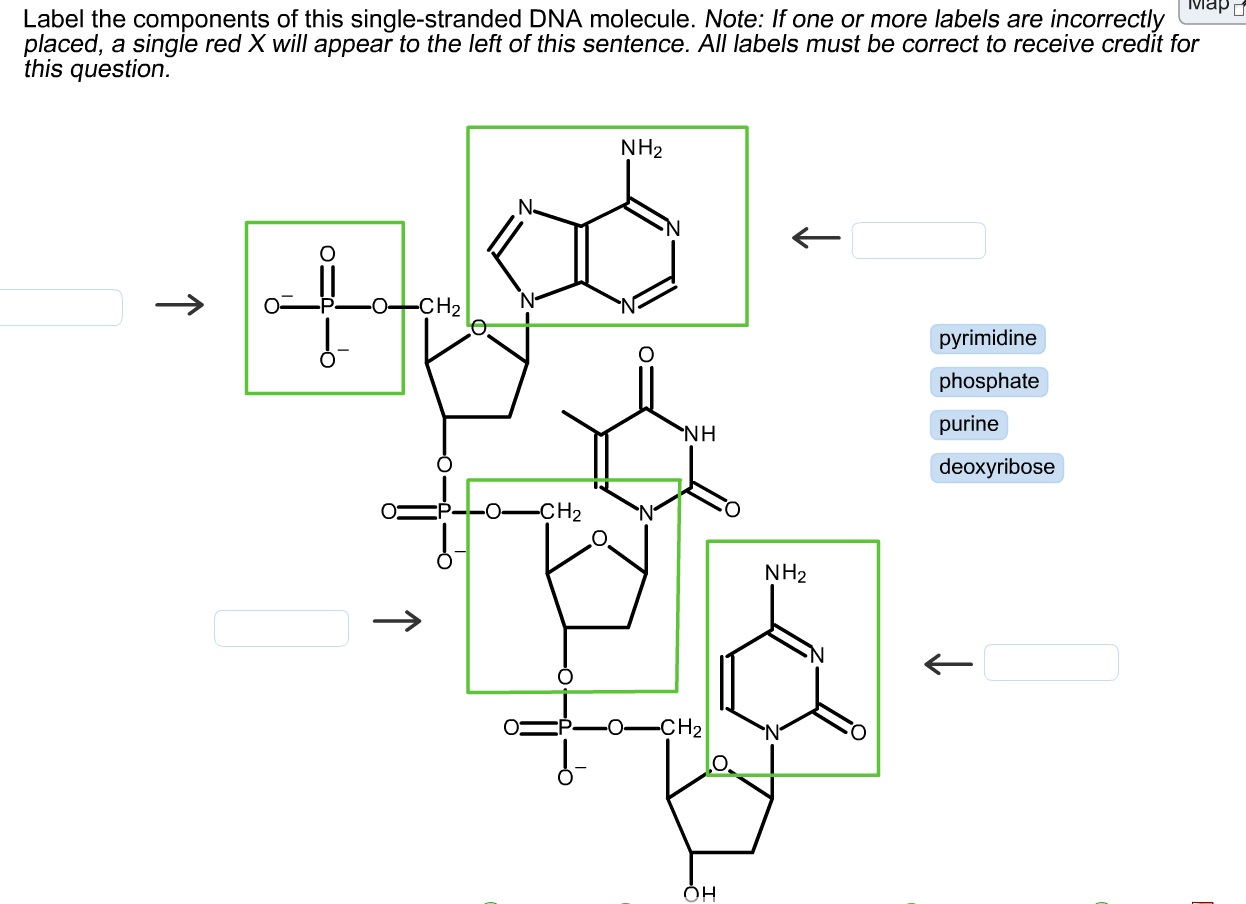


Solved Label The Components Of This Single Stranded Dna M Chegg Com
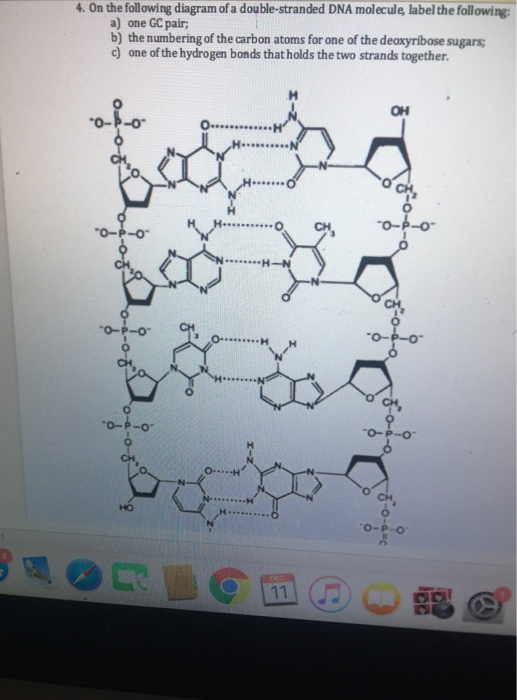


Solved 4 On The Following Diagram Of A Double Stranded D Chegg Com
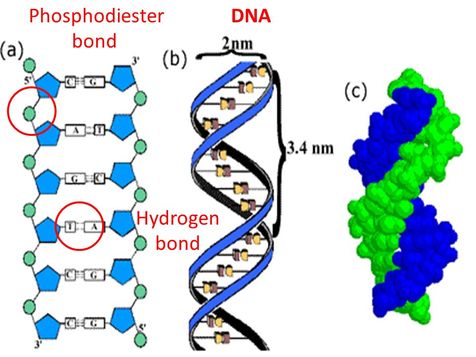


2 6 Dna Rna Structure
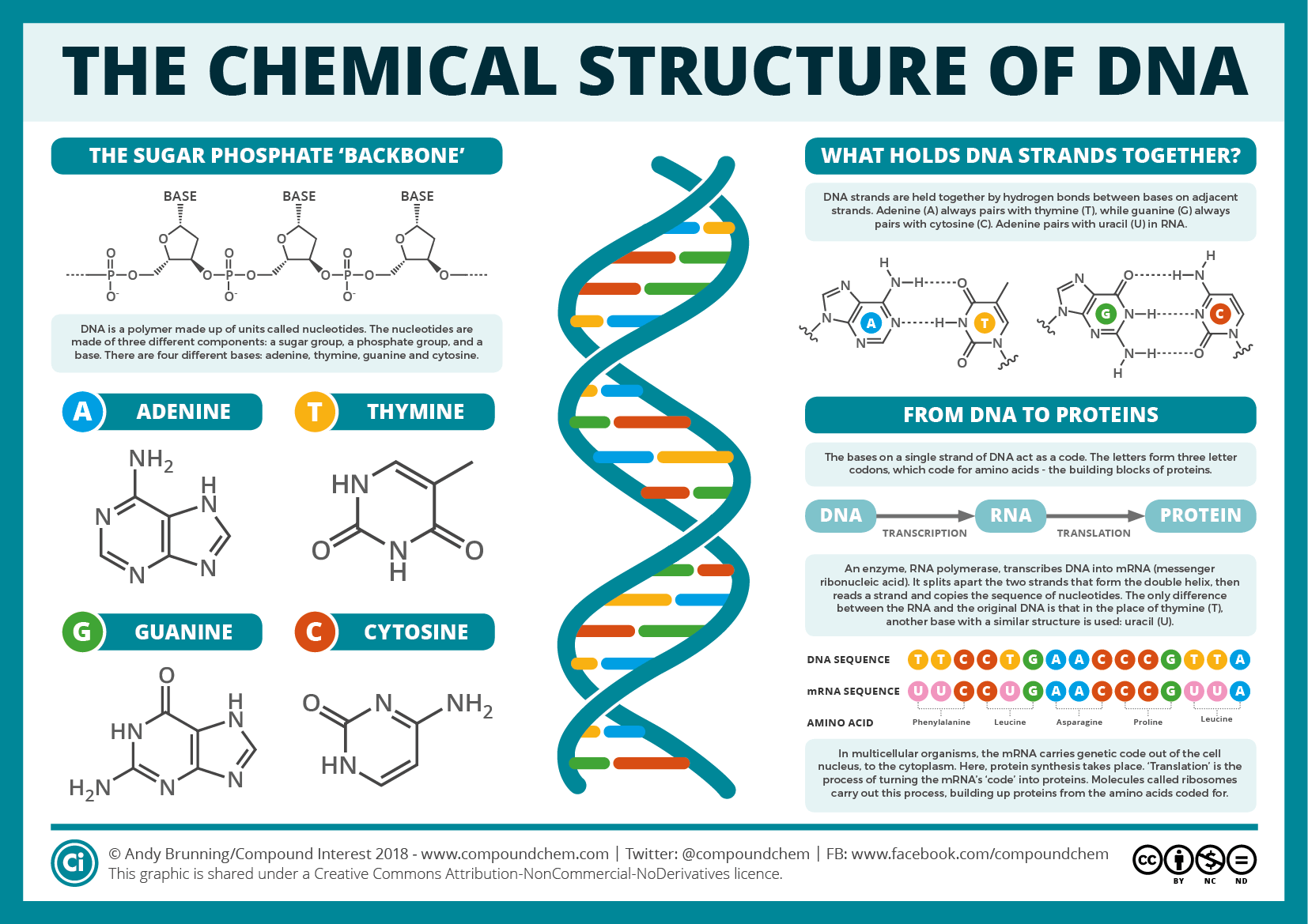


Dna Structure Properties Types Forms Functions
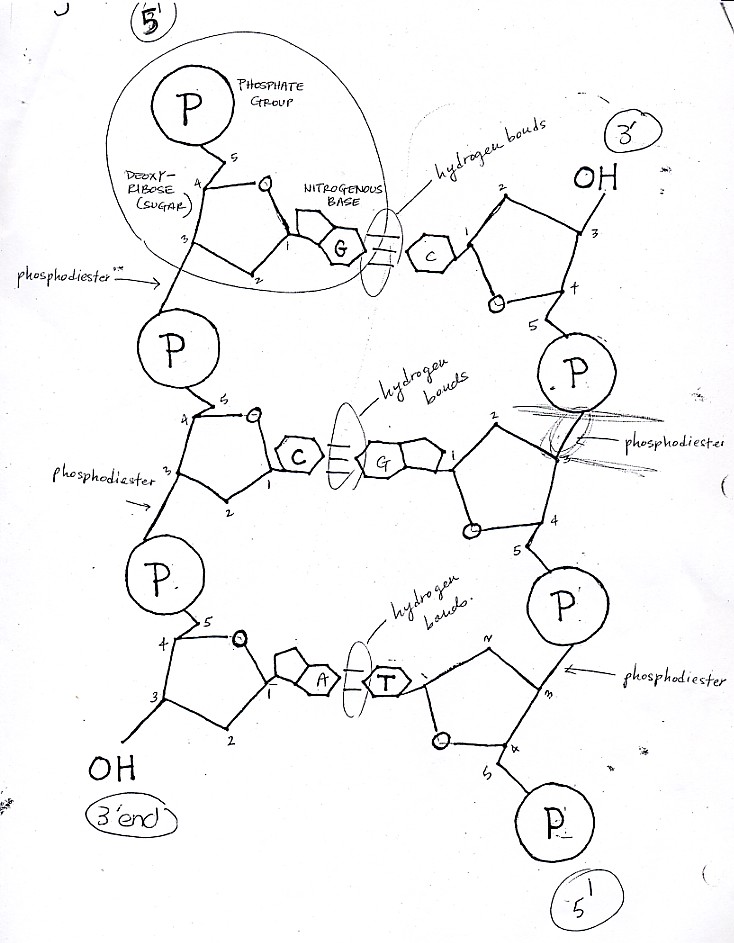


Bioexcel 190 Molecular Genetics Key


Structure Of Dna And Rna



Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable



The Dna Structure Salient Features Dna Helix Packaging Videos Q A



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿